Hair Loss
Hair loss, medically known as Alopecia, is caused by several factors. Knowing these factors and discussing them with us during consultation will help us get a clear picture and hence, will lead to the proper treatment plan to restore the hair loss.
Genetic Factor
Main factor for hair loss, unfortunately it could not be prevented, However, due to the new technology and the our hair restoration techniques, hair loss could be stopped and restored. Hair loss is manifested in a pattern similar to the family members on either side of the family
Diet Factor
Low protein intake, Iron and certain supplements deficiencies: Zinc, Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, Folic acid and Biotin are the main causes.Some people are allergic to the Gluten found in wheat, rye and barley that results in low levels of thyroid hormones which are needed for the hair growth and development.
Psychological Factor
Stress is the number one factor.
Lifestyle Factor
Excessive dieting, Smoking, excessive Alcohol intake and illicit drugs abuse.
Psychiatric Factor
Diseases like Bulimia, Anorexia nervosa and Trichotillomania.
Psychiatric Factor
Diseases like Bulimia, Anorexia nervosa and Trichotillomania.
Medications
such as Lithium, Sodium Valproate, Isotretinoin, excess Vitamin A.
Diseases
Thyroid diseases are the major causes for Hair loss. In addition to anemia, chronic illness and even following a major surgical procedure. Other Hair diseases, defined as cicatricial and non-cicatricial alopecias. Recent studies have shown a big correlation between COVID-19 and hair loss.
Male pattern hair loss
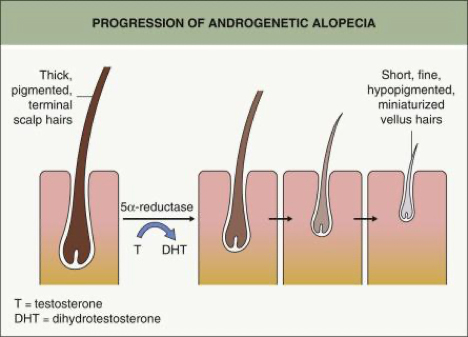
Which is also called androgenetic alopecia, one of the most common causes of hair loss in males. The condition is hereditary where male androgens (Testosterone hormone) becomes Dihydro-Testosterone (DHT) locally in the scalp, which eventually leads the thick hair (Terminal Hair) to start getting thinner and changing into fine hair (Vellus Hair), this process is called miniaturization. The anagen phase of hair becomes shortened, while the telogen phase becomes prolonged than normal conditions.
The pathology of Female pattern hair loss is basically the same as the male pattern hair loss, however the pattern of hair loss in females is different.
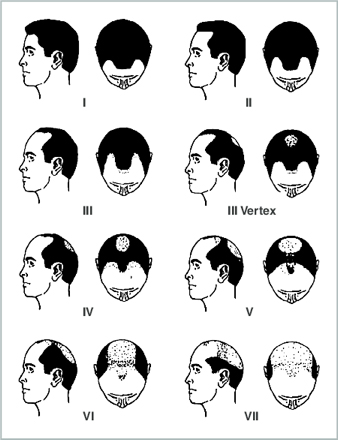
Norwood-Hamilton’s Male pattern hair loss Classification:
The pattern of hair loss in males are classified into 7 Grades
- Grade I: Normal or minimal recession of the frontotemporal angle
- Grade II: Moderate recession of the frontotemporal angle.
- Grade III: Excessive recession of the frontotemporal angle.
- Grade IV: same as Grade III but accompanied with marked hair loss in the crown area. With moderate density bridge of hair in the area in between.
- Grade V: Narrowing of the bridge of hair separating the frontal zone from vertex.
- Grade VI: Loss of the hair bridge connecting the frontal zone to the vertex. Also hair loss becomes extensive laterally and posteriorly.
- Grade VII: Most severe form of male pattern progression
A narrow horseshoe appearance of hair along lateral and posterior sides of the scalp.
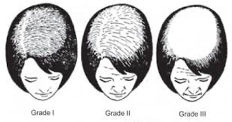
Ludwig’s female pattern hair loss classification:
- Grade I: Minimal global diffuse hair loss across the central scalp.
- Grade II: Moderate global diffuse hair loss across the central scalp.
- Grade III: Severe form of global diffuse hair loss across the central scalp.
Hair loss in females could also be manifested in the form of Christmas-tree Pattern, which is seen as a triangular-shaped hair loss in the central scalp. This pattern is more visible when the patient bends downward and hair is parted in the midline.
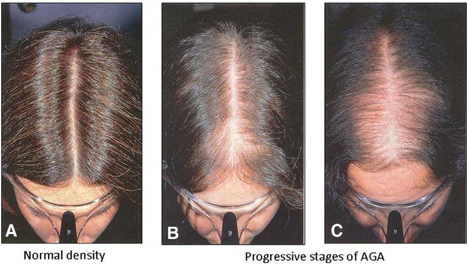
Note that hairline could be spared in females due to the high presence of aromatase hormone, while postmenopausal females could show frontotemporal angle recession similar to male pattern hair loss due to the excessive presence of androgens.
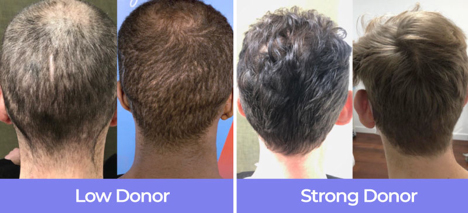
The Donor area
Is referred to the area of hair on the posterior and lateral sides of the scalp. This area is characterized by a heavy density of hair varying from one patient to another. It functions as a finite reservoir of hair which will be used for transplanting the recipient balding area. An average donor area yields from 5,000 to 7,000 hair follicles, non sensitive to the Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which is responsible for the hair miniaturization then hair loss. Therefore, according to Donor Dominance theory, the transplanted hair will not be affected by the circulating androgens in the scalp, thus will not be subjected to loss, and also will take the same characteristics as scalp hair.
In HRKlinik we calculate the Donor area density using a specific device called “Dermoscope”.

Dermoscope gives us insight on how many hair follicles per 1 cm2, aiding us on planning ahead and also helps us in examination of the hair.
A single donor area could yield grafts for hair restoration a couple of sessions if harvested carefully with minimal rate of transection and using combined techniques of hair restoration. Usually 6-8 months are needed between a session and the other.
Beard and Body hair act also as secondary donor options for hair restoration. They are very helpful for those who have minimal density on their scalp donor area, however they have different characteristics than the scalp hair
After knowing now about the grades of hair loss, and about the donor area, we could discuss on the consultation day the long term strategy that is suitable for you to restore your hair loss and provide you with the best results. In HRKlinik we never seek perfection but rather improvement with the best and safest methods for hair restoration.